Daewoo Dual Fuel Forklifts Anaheim
Basic Fuel Types of Forklifts
Powered lift trucks known as forklifts are utilized in almost every business to move heavy items and materials. The forklift is a very durable and reliable equipment which has become essential tools in numerous construction and warehouse settings. Lift truck units differ depending on the type of fuel that is used to power the lift truck and the kind of work environment.
Electricity
Electric powered lift trucks are best for indoor environments, or in sites with limited ventilation because they produce no exhaust fumes. They are designed with industrial strength batteries. Since the electric forklift batteries require charging, the worksite would require a charging station. The batteries are durable and can be re-charged up to 1,500 times before they need to be replaced. The charging station must be situated in a ventilated area and include an acid spill kit and an emergency eyewash station.
Propane
Forklifts powered by liquid propane have some advantages over diesel and electric powered machines making them fairly common in warehouse and industrial settings. Propane engines are much cleaner than diesel-powered units. There is no down time needed to recharge an industrial battery, and the cost for propane is less compared to the cost of electricity. A forklift propane tank could be refueled quickly and easily by changing out the empty tank with a full tank. Normally an off-site supplier refills the empty tank, making refueling very efficient and safe.
Diesel and Gasoline
For outdoor applications and rough terrain, the gas and diesel forklifts are the machines of choice. These machines are fairly common in lumber yards and on construction sites. Their disadvantages comprise fairly high maintenance requirements, odorous exhaust and relatively high fuel costs. Their benefits comprise a longer lifespan compared to other units and dependability in tough conditions. Gasoline and diesel units must be refueled at a supply station on site that meets health and safety regulations.
- Caterpillar Narrow Aisle Forklifts Anaheim
Narrow Aisle Forklift Utilized to both lower and lift loaded pallets from storage spaces that are high is a narrow aisle forklift. This type is recommended for work environments with narrow spaces between aisles, such... More - Toyota Dual Fuel Forklift Anaheim
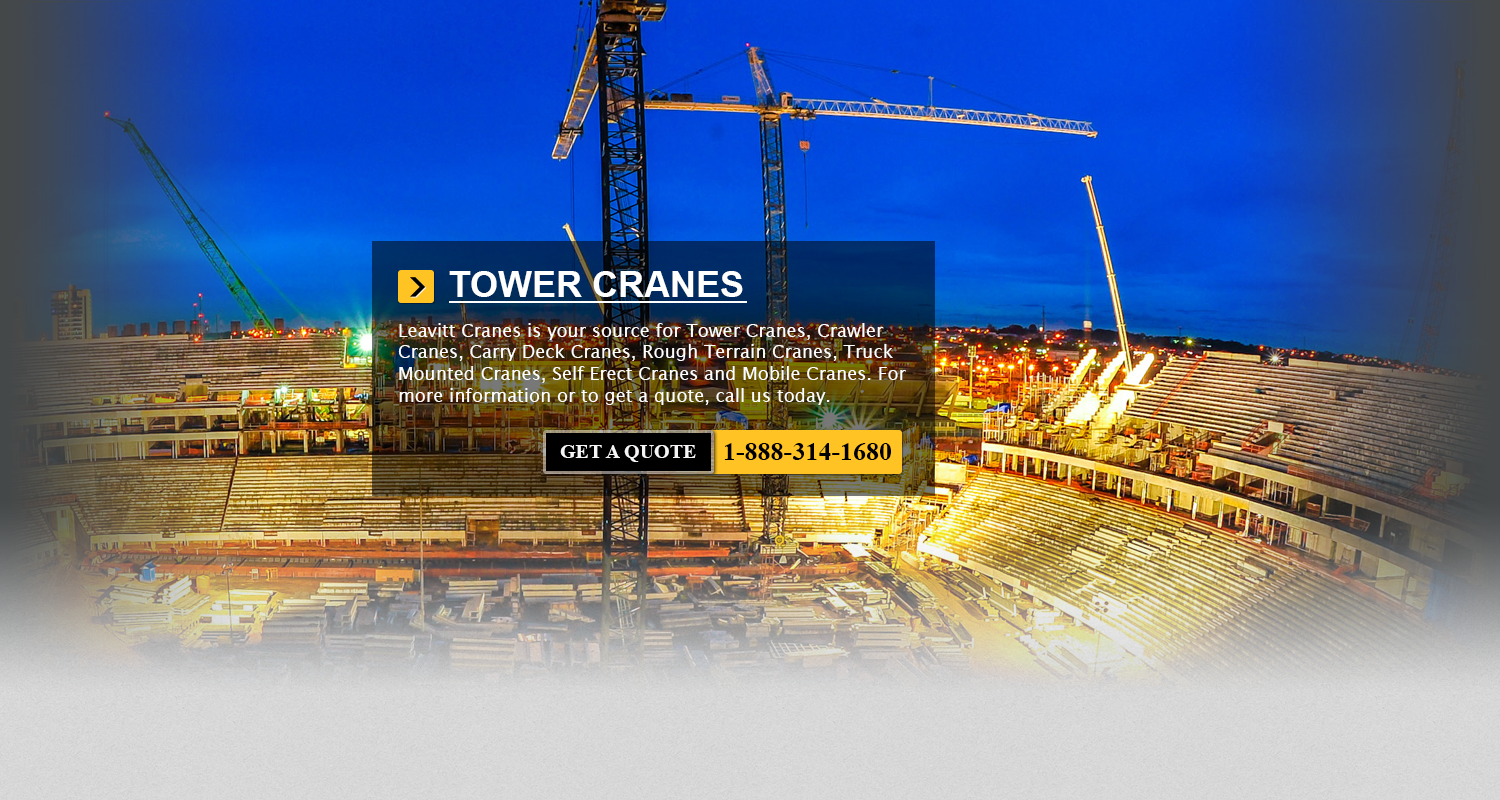
Sakichi Toyoda was the first founder of the Toyota Industries Corporation or TICO during the year 1926. TICO has expanded the scope of its business domains since the companies inception to promote diversification, like logistic... More - Comansa Tower Cranes Anaheim
Since 2011, the Linden Comansa company has offered its clients the LC 1600 series tower cranes. This series includes the models: 16 LC 185, 16 LC 260 and 16 LC 220. These units are available... More - Yale Outdoor Forklift Anaheim
Reach Assembly & Carriage Both the carriage and the reach assembly receive lots of stress throughout a typical work shift. In order to make sure that the truck keeps production levels high, high durability of... More - Mitsubishi IC Forklifts Anaheim
The forklift usage all around the world has grown in insurmountable measures in regards to the warehousing and manufacturing industries. A forklift is a powered industrial truck utilized for lifting and transporting items. The equipment... More